Electric Vehicles: A Pivotal Solution in the Quest for Emission Reduction
As global greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise, the push for sustainable solutions is more urgent than ever. Among the various strategies, electric vehicles (EVs) stand out as a promising alternative. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global sales of EVs soared to 14 million units in 2023, making up 18% of all vehicle sales—a significant increase from the previous year.
The growing presence of EVs has shifted the focus to efficient charging and discharging processes, leading to a surge in research activities. Key areas of study include optimizing charging station layouts, analyzing driver charging behaviors, predicting charging loads, and managing charging networks. These efforts rely heavily on comprehensive charging transaction datasets, which are instrumental for data mining, machine learning, and simulation modeling. Through these technologies, patterns can be identified, demand predicted, and decision-making optimized.
Numerous datasets documenting EV charging transactions are now accessible to the public. For instance, the Electric Vehicle Charging Dataset utilizes advanced methods like Conditional Tabular Generative Adversarial Networks (CTGAN) and Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) to model user behavior. Similarly, the Leeds City Council dataset offers minute-by-minute data from 2014 to 2021, providing insights into charging habits within a specific area. Another noteworthy dataset captures high-resolution workplace charging data, detailing vehicle types and commute distances to better understand user perspectives.
Despite the availability of these datasets, certain challenges persist. Many datasets cover limited timeframes or locations, hindering their broader applicability. Simulation data, often based on specific assumptions, can be difficult to verify. Additionally, most datasets focus primarily on the transaction process without considering user intent or external factors like weather.
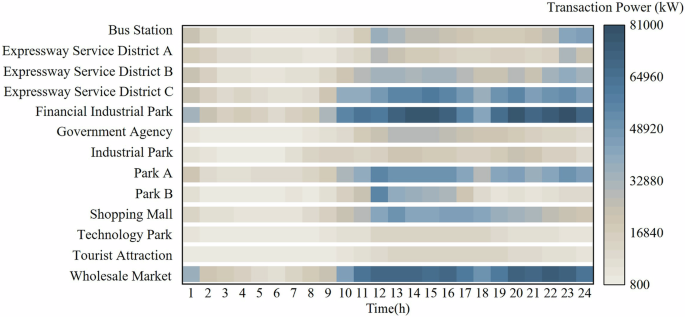
Addressing these gaps, a new comprehensive dataset has been developed to offer enriched information across diverse spatial dimensions. This dataset includes charging transactions in urban and suburban areas of a Chinese city, complete with user IDs, precise timing of charging sessions, electricity volumes, costs, reasons for transaction termination, and weather conditions. Organized by station location, this dataset facilitates streamlined processing and offers valuable applications in several domains:
1) Enhancing User Experience
By analyzing user charging behavior, the layout of charging stations can be adjusted to improve user experience.
2) Policy and Market Strategy Evaluation
The dataset aids in assessing the effectiveness of EV support policies and refining market strategies.
3) Weather Impact Analysis
Data on weather conditions can be used to study their impact on battery performance and charging habits, assisting in load prediction and simulation.
4) Equipment Stability and Reliability
An analysis of charging stack failures can provide insights into equipment reliability, guiding maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
Original Story at www.nature.com