By Zoe Kleinman,Technology editor
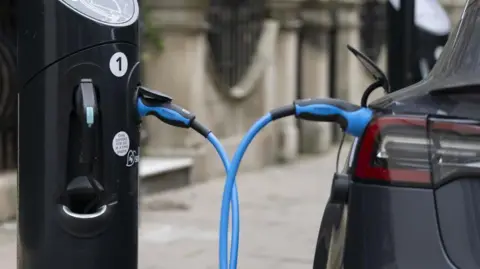
Getty Images
An electric car battery developed by UK start-up Nyobolt has successfully charged from 10% to 80% in four minutes and 37 seconds during its first live demonstration.
The achievement took place with a specially-built concept sports car on a test track in Bedford, marking significant progress in efforts to increase electric vehicle (EV) charging speeds.
In comparison, a Tesla supercharger typically takes 15-20 minutes to charge a car battery to 80%.
Experts emphasize the need to eliminate “range anxiety” to boost EV adoption and stress the importance of improving the charging infrastructure.
“Developing technology that enables quicker charging, comparable to traditional refueling times, is crucial,” said Paul Shearing, Professor of Sustainable Energy Engineering at Oxford University.
Shearing added that there needs to be more chargers of all types.
The tested sports car achieved a range of 120 miles after four minutes of charging. By contrast, a Tesla charged to 80% can typically reach up to 200 miles.

Nyobolt
Dr. Sai Shivareddy, co-founder of Nyobolt, expressed satisfaction with the results but admitted the tests were “nerve-wracking.”
The demo, conducted live in front of industry professionals, faced challenges, including the UK heatwave and a failure in the car’s cooling system.
These factors prevented the team from recreating laboratory results, where the battery charges from 0% to 100% in six minutes.
Despite this, Dr. Shivareddy described the event as “a milestone for electrification” and humorously noted his own car was still charging since he arrived earlier that day.

Nyobolt
Nyobolt plans to partner with existing car brands rather than manufacturing its own vehicles, potentially integrating the battery into EVs “at small scale” within a year.
While 350kW DC superfast chargers needed for such batteries are available in the UK, they are not yet widespread.
Nyobolt claims minimal degradation, stating the battery retains 80% charge after 4,000 cycles.
A full cycle is a charge from 0-100%, but this can be split into multiple smaller charges. For context, Apple claims the iPhone 15 battery will maintain 80% functionality after 1,000 cycles.

Nyobolt
Power, Weight, and Durability
The global race to develop faster-charging batteries that are more powerful, lighter, and durable continues. Last year, Toyota announced a breakthrough enabling a solid-state battery that charges in ten minutes and lasts 1,200 km (754 miles).
US start-up Gravity has developed a compact charger that adds 200 miles of range in under 13 minutes.
However, Dr. Edward Brightman, a lecturer in chemical engineering at Strathclyde University, noted that while rapid charging is beneficial for long journeys, the main barrier to EV adoption lies in the supporting infrastructure.
“Electric cars aren’t limited by the batteries anymore,” he said. “We urgently need to upgrade the grid and deploy rapid chargers to deliver the necessary charge.”
Original Story at www.bbc.com
