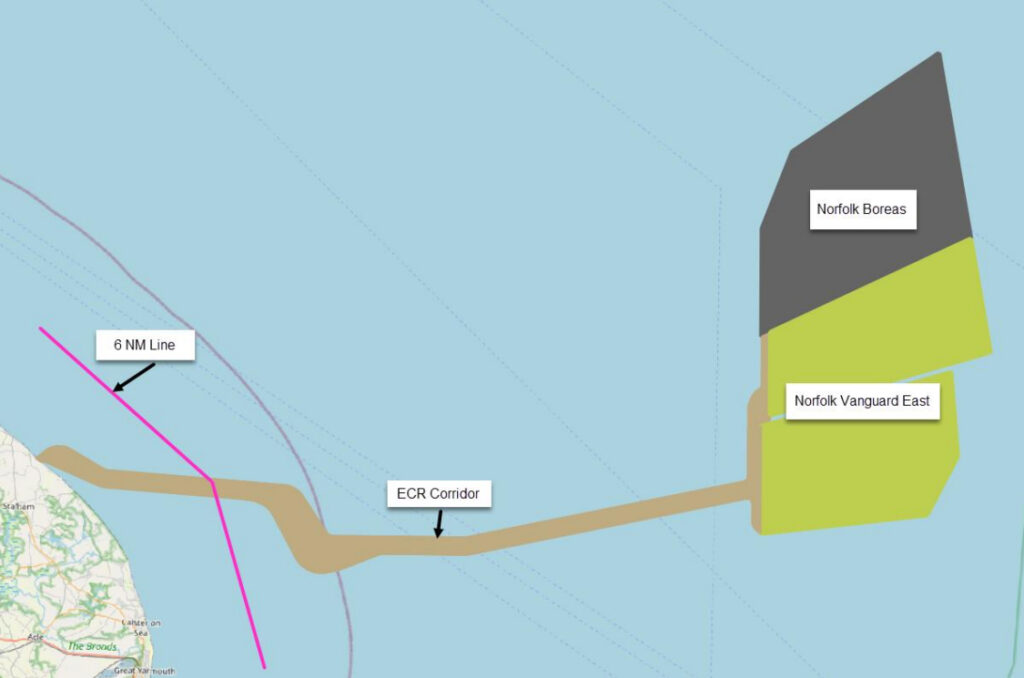
RWE has initiated geophysical and geotechnical site investigations at its Norfolk Boreas, Norfolk Vanguard East, and Norfolk Vanguard West offshore wind project sites in the UK, acquired from Vattenfall earlier this year.
The survey vessel Braveheart Spirit is conducting geotechnical survey operations within the Norfolk Boreas and Norfolk Vanguard East offshore wind farm sites. The shallow geotechnical scope includes in situ measurements, sampling, cone penetration testing (CPT), and vibrocore. The survey campaign, which began recently, is expected to last three months.
At the Norfolk Vanguard East site, geophysical and seismic surveys have been ongoing since June, with the vessels Geo Ranger, Noordhoek Pathfinder, and Geo Focus deployed for the work.
Geo Ranger and Noordhoek Pathfinder are performing geophysical surveys within the Norfolk Vanguard East site and along the export corridor boundaries. These surveys are anticipated to continue until the end of 2024, weather permitting.
The Geo Focus survey vessel is tasked with seismic surveys within the Norfolk Vanguard East site, expected to be completed by the end of October.
Geo Focus and Noordhoek Pathfinder began their assignments on RWE’s Norfolk offshore wind portfolio in May with geophysical surveys at the Norfolk Vanguard West site.
The Norfolk Boreas, Norfolk Vanguard East, and Norfolk Vanguard West projects are part of the larger Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone, designed to generate enough electricity to power nearly 3.9 million UK homes once operational.
Each of the three projects—Norfolk Vanguard West, Norfolk Vanguard East, and Norfolk Boreas—has a planned capacity of 1.4 GW and is located 50 to 80 kilometers off the Norfolk coast in East Anglia.
Initially developed by Vattenfall and acquired by RWE in March 2024, the projects have secured seabed rights, grid connections, Development Consent Orders, and other key permits. The Norfolk Vanguard West and East projects are the most advanced, with key components already procured.
Upon acquiring the projects, RWE stated that the next milestone for the Norfolk Vanguard West and Norfolk Vanguard East projects was to secure a Contract for Difference (CfD) in upcoming auctions.
RWE also resumed the development of the Norfolk Boreas project, which was previously halted.
Original Story at www.offshorewind.biz