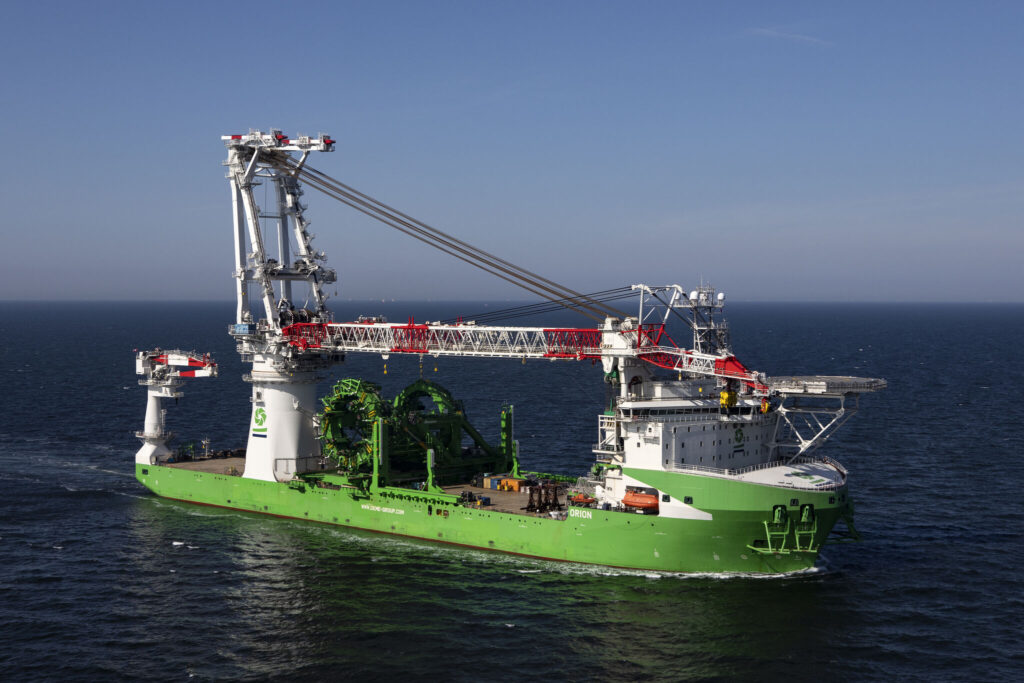
The DP3 installation vessel Orion, operated by Belgian offshore specialist DEME, is set to install the remaining monopile foundations at Vineyard Wind 1 in the US around 28 October, according to a recent offshore wind mariner update.
Before installation, vessels POLARIS and HOS RUGER will deploy and recover a double big bubble curtain (DBBC) system to manage pile-driving operations.
The DBBC will be set up on the seafloor, tested, and activated before Orion arrives. Each bubble curtain takes about two to four hours to install, as reported by Vineyard Wind, a partnership between Avangrid and Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP).
After pile-driving, POLARIS and HOS RUGER will retrieve the DBBC equipment for use at the next site.
Upon completing monopile installation, DEME Group’s jack-up vessel, Sea Challenger, will install transition pieces (TPs) at the sites starting in early November. The operation will be supported by vessels GO FREEDOM, GO PATRIOT, and GO GLORY.
DEME Offshore US is leading the transportation and installation of monopile foundations, TPs, offshore substations, scour protection, and wind turbines.
The first of 62 monopile foundations, supplied by EEW Special Pipe Constructions (EEW SPC), was installed 15 miles off Martha’s Vineyard in June 2023.
The 800 MW offshore wind farm will feature 62 GE Vernova Haliade-X 13 MW wind turbines, each with a 220-meter rotor and 107-meter blades.
Earlier this year, a turbine blade broke due to a manufacturing issue, as reported by the company’s CEO Scott Strazik in July.
In July, the US Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement (BSEE) ordered Vineyard Wind to halt electricity production until further examination of the blade failure’s impact on other turbines.
In mid-August, authorization was granted to resume certain activities, leading to the installation of eight new towers and nacelles, as noted by Vineyard Wind.
Last week, Vineyard Wind announced that GE Vernova plans to remove some blades and reinforce others as part of their incident response plan.
Follow offshoreWIND.biz on:
Original Story at www.offshorewind.biz
